Lighting Interactive Design - Weekly Note
MODULE INFORMATION BOOKLET
Week 1 (3/2/2025) – Introduction to Lighting Interactive Design
Class Summary
Today's class introduced us to lighting interactive design, focusing on projection mapping and immersive experiences.
Lecture Notes
Concepts
- Transform buildings by giving them different unique looks and personalities.
- Create immersive experiences, particularly for indoor spaces.
Key Considerations
- Canvas – Understand the building or structure that are being mapped.
- Scale – Ensure visuals are properly adjusted to match real-world size.
- Light & Shadow – Use depth effects to create a 3D illusions.
- Creativity – Think outside the box to make engaging and dynamic visuals.
Tools & Software
Assignment Details (Assignment will be in GROUP *Except of Portfolio*)
- Exhibition Venue: Muzium Telekom
- Duration: 1 minute
- Surface: 3 walls, 1 floor
**Wednesday Go to Muzium Telekom (5/2/25)**
Week 1 (6/2/2025) – Muzium Telekom ( Site Visit )
Class Summary - In today's class, we had a short lecture at Muzium Telekom. We explored the space, which gave us a better understanding and inspired new ideas for our project.
How to Determine a Suitable Projection Surface
- Canvas Color: Use white or light-colored surfaces since projection light is primarily white.
- Black Background: If the surface is black, the projection will appear gray and less vibrant.
- Material: The surface must be matte and non-transparent to prevent light from passing through.
Choosing the Right Building for Projection Mapping
- Modern buildings often have too much glass, making them unsuitable for projection.
- Heritage or vintage buildings are ideal as they are mostly white, feature-rich, and have smaller sections to experiment with.
- Ensure there is a clear projection path—a space to position the projector at the right height and angle.
- A common issue in Malaysia is obstructed views due to roads and parked cars, so the viewing location must be carefully planned.
How to Start
- Develop an Idea & Concept
- Use a mind map to expand ideas.
- Extract key keywords from the concept.
- Start gathering visual references (mood board, sketches).
- Focus on the Visuals First!
** Do not think about movement yet—prioritize static visuals.
** The final projection will be 1 minute long, with 10 seconds per scene.
Week 2 (10/2/2025)
1. Understanding Projection Mapping
Projection mapping is a technique that transforms surfaces (buildings, sculptures, logos, etc.) into dynamic visual displays. To create effective content, consider:
- The Canvas: Type of surface, scale, and how content fits.
- Light & Shadow: Enhancing visual depth for realism.
- Creativity: Pushing artistic and technical possibilities.
2. Technical Setup & Execution
Understanding the Canvas
- Obtain the layout and measurements of the building.
- Compress measurements to 1080px for projection planning.
- Assess the room setup to determine the best projector placement.
Projection Selection
- Select a projector type based on brightness, resolution, and projection surface.
- Obtain measurements of the projector and lens specifications.
- Use a projector calculator to determine:
- Distance & height of the projector.
- Number of projectors required.
- Optimal projection angle.
- Whether the light intensity is sufficient for the distance and lens used.
Rigging Setup
- Large-scale outdoor projections may require a crane to position the projector.
- Setup usually takes about a week, including calibration and connections.
- Addressing obstacles:
- A tree blocking a projector may require repositioning it slightly inward.
- Another solution is to raise the projector and angle it downward for proper coverage.
3. Planning & Concept Development
Step 1: Brainstorming & Mind Mapping
- Generate ideas, themes, and visual concepts.
- Identify key messages and artistic direction.
Step 2: Understanding the Projection Canvas
- Assess building/site structure for feasibility.
- Consider environmental factors (size, angles, obstructions).
4. Industry Workflow: Two Teams Working Simultaneously
Technical Team
- Handles hardware setup, projector calibration, and execution.
- Ensures proper lens shift & rotation (adjusting the projector without moving it).
Creative Team
- Focuses on visual content creation using a structured process:
Creative Team Workflow
- Idea & Brainstorming – Develop initial concepts and visual themes.
- 3D Visualization (Front Side Only) – Create models using Blender or similar 3D software.
- Storyboard & Style Frames – Sketch the flow of visuals.
- Tools: Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Procreate.
- Sent to client for approval.
- 2D & 3D Animation – Develop motion graphics.
- Tools: After Effects, Cinema 4D.
- Final Compositing – Add effects, sound, and final refinements.
- Tools: Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, Adobe Audition.
- Projection Mapping Execution – Apply animations to real-world surfaces.
- Tools: Resolume Arena, MadMapper.
5. Sketches, Storyboarding & Animatic
Sketches & Storyboarding
- Purpose: Define form, shape, and sequence before digital execution.
- Sketches & Storyboards are interchangeable – can be shuffled and reused.
- Descriptions should be clear and detailed for better communication.
Animatic (Expected for Final Submission)
- A rough animation preview combining sketches with sound.
- Helps refine timing, transitions, and overall flow.
- Tools: CapCut (allowed for this assignment).
Sketch Example
6. Assignment Submission Requirements
Portfolio - Your portfolio should document the entire process:
- ✅ Attach MIB & Assignment Brief (NO slides needed).
- ✅ Show weekly progress & process development.
- ✅ Include first and second attempts to illustrate refinement.
- ✅ Write a final reflection on what was learned.
- ✅ Use visual aids for clarity.
- ✅ Document lecturer feedback in the blog.
Week 3 (19/2/2025)
Class Notes – Animation and Video Editing
Today's lecture started with a recap of the previous class, followed by inspiration videos showcasing projection mapping on buildings.
Principles of Animation
These principles help make animation look more believable and engaging:
- Squash and Stretch – Movement that squashes and stretches (e.g., a ball squashes when it hits the ground and stretches when it bounces). This effect is exaggerated in animation.
- Anticipation – A preparatory movement before the main action occurs (e.g., a character bending knees before jumping).
- Follow Through & Overlapping Action – Elements continue moving even after the main action stops (e.g., a character’s hair or clothing following the motion).
- Arcs – Natural movement follows a curved path rather than a straight line.
- Slow In & Slow Out – Gradual acceleration and deceleration for smoother motion.
- Timing – Controlling the speed of movement (a technical aspect of animation).
- Secondary Action – Additional movements that complement the main action (e.g., a character swinging their arms while walking).
- Exaggeration – Enhancing movement for dramatic or comedic effect.
- Staging – Directing the audience’s attention to the most important part of the scene.
- Straight Ahead & Pose-to-Pose Animation –
- Straight Ahead: Frame-by-frame animation for more fluid motion.
- Pose-to-Pose: Key poses are created first, then in-between frames are added (common in Blender).
- Solid Drawing – Giving 3D depth to 2D animation.
- Appeal – Making characters visually interesting and engaging.
Animation vs. Motion Graphics
- Animation: Creating movement for storytelling, characters, and realistic motion.
- Motion Graphics: Moving graphic elements and shapes, often used for marketing and digital design.
Usage of Motion Graphics
- Social media posts
- Digital posters
- Animation and film
- Projection mapping
- Exhibitions
Motion Graphics Applications
- Adobe After Effects – Industry standard (80% usage). Requires a subscription.
- Nuke – Used in high-end visual effects (20% usage).
- Rive – Focuses on interactive animations.
- Fable – Has limitations in detail and uses presets.
- Figma – Mostly for UI/UX design but supports animations.
- Blender – Can create both 2D and 3D animations.
- Calvary – Similar to Fable but with limitations in complexity.
Video Editing Techniques
Today's lesson included learning the basics of Adobe After Effects, a key tool for motion graphics and animation.
Week 4 (24/2/2025)
Class Notes
In today's class, we received a briefing on Assignment 2 and having lecture about Narrative and Concept Development.
Projection Mapping Overview
- Transforms spaces with dynamic visuals.
- Used in art, ads, events, and heritage sites.
- Narrative Outline – Guides storytelling.
- Moodboard – Defines visual style.
- Storyboard – Plans scene sequences.
- Framework for visual content.
- Ensures logical flow & emotional impact.
- Title, Objective, Audience, Theme.
- Characters & Setting – Who & where.
- Includes images, colors, textures, typography, animations.
- Ensures consistent style.
- Visualizes script into scenes.
- Defines angles, transitions, effects.
Week 5 (05/3/2025)
Class Notes (how to import asset from PS or AI to After effect)
Size : 1700 px x 3840 px
Importing Assets from Photoshop to After Effects
- When transferring elements from Photoshop to After Effects, ensure that all objects are placed in separate layers.
- If you import the file into After Effects and later add a new layer in Photoshop, it will not appear in After Effects. However, if you add elements to an existing layer, those changes will be reflected.
- To import the Photoshop file into After Effects, select "Composition - Retain Layer Sizes" to preserve the individual layers.
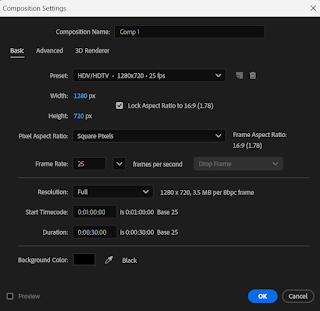
Figure 5.1 Setting when drag in any things into Adobe after effect
Working with Layers and Pre-Compositions in After Effects
- If you press Ctrl + C, create a new composition, and paste elements inside, any changes made to the original layer will update automatically.
- Use Ctrl + Shift + C to create a pre-composition that groups all selected layers together, treating them as a single unit.
Adding Effects in Adobe After Effects
- After importing Photoshop assets, various effects can be applied to enhance the animation and visual appeal.
- Experiment with keyframes, transitions, and blending modes to create dynamic motion graphics.
- KeyLight -Remove many unwanted Color
Short Cut Key
- ctrl + D = Duplicate
- Ctrl + Shift + C = pre-composition
1. Alpha Matte & Masking Shapes
- Alpha Matte: A new function in After Effects that allows masking effects within a shape.
- Making Shape Edges Blue:
- Apply a Blur Effect and adjust the settings accordingly.
- Another method: Use Mask Feather to create a soft, blurry edge.
2. Puppet Tool
- Used for simple animations on objects like hands, figures, or other elements.
- Allows you to create joints on a character and move them for animation.
3. Parenting
- All child layers follow a single parent layer.
- Useful for animating multiple objects together.
4. Wiggle Effect on Scale
- Press Alt + Click on the Scale property.
- Adjust settings manually or use an expression (code) to control the effect.
5. Plugins for Effects
- Websites to find After Effects plugins:
- Motion Array
- AEScripts
6. Rendering in After Effects
Method 1: Directly from After Effects
- File → Add to Render Queue
- Select the Best Settings below
- Format: H.264
- Choose the export destination
- Click Render
Method 2: Exporting with Transparent Background
- Output Settings: Change H.264 to QuickTime
- In Video Output, select Alpha or RGB+Alpha
Method 3: Using Adobe Media Encoder
- File → Add to Adobe Media Encoder Queue
- Select and change the format settings as needed
- Click Render
Note:
- Rendering in After Effects requires waiting until completion.
- Adobe Media Encoder allows you to continue working while rendering.
7. Render Output Settings
- Resolution: 3840 x 1700 px
- Audio: Included
- Frame Rate: 25 FPS
- Color Depth: Minimum 8-bit
- Format: MOV / MP4
8. Keyframe Shortcut
- Press U to see all created keyframes.
Connecting to a Projector
To connect to a projector, follow these steps:
- Physical Connection – Use an HDMI, VGA, or DisplayPort cable to connect your computer to the projector.
- Display Settings – Adjust your computer’s display settings to extend or duplicate the screen.
- Projector Settings – Ensure the correct input source is selected on the projector.
Learning Resolume Arena
- Resolume Arena allows us to map and control projection visuals.
- Input vs. Output:
- Input refers to the selected visual content.
- Output is the projection displayed onto a surface.
- We can select and map specific parts of an image or video to align with a mock-up, adjusting section by section.
- It's possible to create a new screen and map it separately if needed.








Comments
Post a Comment